Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Aerospace Laser Technology and Systems Department, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Shanghai Typhoon Institute, China Meteorological Administration, Shanghai 200030, China
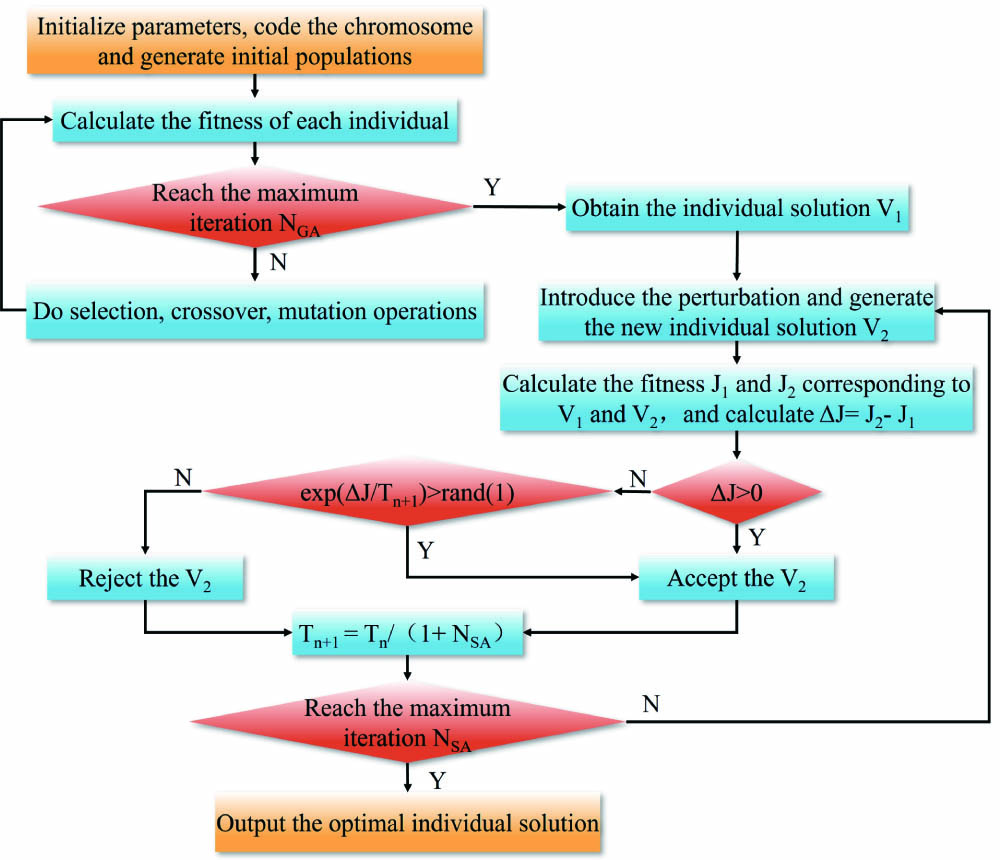
A method of spectrum estimation based on the genetic simulated annealing (GSA) algorithm is proposed, which is applied to retrieve the three-dimensional wind field of typhoon Nangka observed by our research group. Compared to the genetic algorithm (GA), the GSA algorithm not only extends the detection range and guarantees the accuracy of retrieval results but also demonstrates a faster retrieval speed. Experimental results indicate that both the GA and GSA algorithms can enhance the detection range by 35% more than the least squares method. However, the convergence speed of the GSA algorithm is 17 times faster than that of the GA, which is more beneficial for real-time data processing.
coherent Doppler lidar three-dimensional wind field retrieval genetic simulated annealing algorithm spectrum estimation typhoon Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(4): 040101

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518055, China
Single-molecule localization microscopy (SMLM) enables three-dimensional (3D) investigation of nanoscale structures in biological samples, offering unique insights into their organization. However, traditional 3D super-resolution microscopy using high numerical aperture (NA) objectives is limited by imaging depth of field (DOF), restricting their practical application to relatively thin biological samples. Here, we developed a unified solution for thick sample super-resolution imaging using a deformable mirror (DM) which served for fast remote focusing, optimized point spread function (PSF) engineering, and accurate aberration correction. By effectively correcting the system aberrations introduced during remote focusing and sample aberrations at different imaging depths, we achieved high-accuracy, large DOF imaging () of the whole-cell organelles [i.e., nuclear pore complex (NPC), microtubules, and mitochondria] with a nearly uniform resolution of approximately 35 nm across the entire cellular volume.
Photonics Research
2024, 12(4): 821
1 天津大学精密仪器与光电子工程学院,天津 300072
2 天津大学光电信息技术教育部重点实验室,天津 300072
基于商用单模掺铥石英光纤设计了高功率2.05 μm波段全光纤主振荡功率放大器(MOPA)。以自制环形腔掺铥光纤激光器为种子,利用级联滤波型波分复用器优化长波长种子的光信噪比,基于MOPA结构实现了高效的高功率输出。基于速率方程模型,理论分析了主放大级的注入信号光功率和增益光纤长度的优化关系;实验中在102.6 W的793 nm泵浦功率下获得了输出功率为57 W、光谱线宽为0.08 nm、光信噪比为58.8 dB的单横模激光输出,主放大级斜效率为52.6%。
激光器 掺铥光纤激光器 2 μm激光 单模光纤激光器 速率方程
1 天津大学精密仪器与光电子工程学院,天津 300072
2 天津大学光电信息技术教育部重点实验室,天津 300072
3 深圳大学物理与光电工程学院光电子器件与系统教育部/广东省重点实验室,广东 深圳 518060
报道了基于掺铥光纤可饱和吸收体的单频2.05 μm线性腔铥钬共掺全光纤振荡器。腔内采用4.6 m长的铥钬共掺光纤作为增益介质,并利用未被泵浦的掺铥光纤作为可饱和吸收体实现选频,通过调整可饱和吸收体的长度可优化选频能力。在3.5 W的1570 nm激光泵浦下,获得了最高714 mW的2048.6 nm单频激光输出,相应的斜率效率为25.1%,激光光谱线宽为17 kHz。
激光器 单频光纤激光器 铥钬共掺光纤 可饱和吸收体 2 μm激光
1 天津大学精密仪器与光电子工程学院,天津 300072
2 天津大学光电信息技术教育部重点实验室,天津 300072
3 东南大学成贤学院,江苏 南京 210088
报道了基于Nd∶YVO4激光晶体和钨酸钆钾(KGW)拉曼晶体的端面泵浦连续波内腔拉曼激光器,实验研究了基频激光偏振方向对KGW拉曼激光器输出功率、光谱和模式特性的影响。当基频光偏振方向平行于KGW晶体的Nm轴时,901 cm-1拉曼频移增益较高,在36.6 W半导体激光泵浦功率下获得了6.63 W的 1177.3 nm连续波斯托克斯光输出,光光效率和斜效率分别为18.1%和24.7%;而当基频光沿KGW晶体Ng轴偏振时,由于768 cm-1和901 cm-1两条拉曼谱线的竞争以及对应89 cm-1小波数拉曼峰的级联拉曼斯托克斯光起振,拉曼激光器的光谱和功率特性均发生劣化。在实验中还观察到KGW像散的热透镜效应对激光模式产生的影响。
激光器 受激拉曼散射 连续波拉曼激光器 内腔拉曼激光器 钨酸钆钾晶体
1 天津大学 精密仪器与光电子工程学院,天津
2 天津大学 光电信息技术教育部重点实验室,天津
作为最具代表性的定向能载体,激光可用于高功率、长距离的无线能量传输。传统上激光无线传能一般通过跟瞄系统实现,而近年来发展的谐振激光自适应无线传能技术提供了一种无需跟瞄的新解决思路,受到广泛关注。文中分析比较了这两种方法的特点,展望了未来发展趋势,并对后者的核心免调试激光器的实现方法进行了总结。
激光无线传能 谐振激光传能 免调试激光器 猫眼逆反射器 wireless laser power transmission resonant laser power transmission alignment-free laser cat-eye retroreflector
1 中国石油集团工程材料研究院有限公司,西安 710000
2 西南石油大学新能源与材料学院,成都 650100
3 中国石油集团西部钻探工程有限公司工程技术研究院,克拉玛依 834000
针对CO2易腐蚀硅酸盐水泥石、破坏水泥石结构完整性、诱发层间封隔失效等问题,本文利用矿渣改性铝酸钙水泥,研究了铝酸钙水泥-矿渣体系在60、80、100、120 ℃和纯CO2条件下的抗压强度变化规律,并采用X射线衍射仪、热重分析仪和扫描电子显微镜测试了CO2腐蚀对铝酸钙水泥-矿渣体系水化产物及微观结构的影响。结果表明: 与纯铝酸钙水泥石相比,矿渣使铝酸钙水泥石水化产物转变为C2ASH8,大幅提高了水泥石早期抗压强度。当铝酸钙水泥与矿渣质量比为5∶5时,60 ℃养护14 d的铝酸钙水泥抗压强度提高了215.4%。经CO2腐蚀后,铝酸钙水泥-矿渣体系水化产物由C2ASH8转变为C2AS,并有CaCO3生成,腐蚀层的致密程度增加,相同温度下水泥石的抗压强度随腐蚀时间增加而增大。
铝酸钙水泥 矿渣 固井 CO2腐蚀 水化产物 微观结构 calcium aluminate cement slag cementing CO2 corrosion hydration product microstructure
1 景德镇陶瓷大学材料科学与工程学院,江西 景德镇 333001
2 浙江大学材料科学与工程学院,杭州 310058
在陶瓷的常规制备方法中,高温烧结一直是获得致密微结构和优良性能的必要条件。近年来兴起的冷烧结(CSP)技术通过溶解-沉淀等机理,能在350 ℃以内的超低温条件下实现多种陶瓷材料的快速致密化,有效应对了常规高温烧结在能耗、微结构控制及与有机物共烧等方面存在的问题,具有巨大的发展空间和潜力。本文综述了冷烧结的发展历史、工艺流程和致密化机理,对冷烧结技术在陶瓷材料制备中的应用现状进行了概述,涉及生物陶瓷材料、新能源材料、半导体材料、介电材料、热电材料、高温下不稳定材料等,并展望了冷烧结的未来发展趋势。
冷烧结 陶瓷材料 应用 超低温 cold sintering process ceramic materials applications ultra-low temperature
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Fudan University, Academy for Engineering and Technology, Shanghai, P. R. China
2 Tianjin Center for Medical Device Evaluation and Inspection, Tianjin, P. R. China
3 Shanghai University, School of Communication & Information Engineering, Shanghai, P. R. China
4 Fudan University, Center for Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai, P. R. China
5 Fudan University, State Key Laboratory of Medical Neurobiology, Institutes of Brain Science, Shanghai, P. R. China
Automatic cell counting provides an effective tool for medical research and diagnosis. Currently, cell counting can be completed by transmitted-light microscope, however, it requires expert knowledge and the counting accuracy which is unsatisfied for overlapped cells. Further, the image-translation-based detection method has been proposed and the potential has been shown to accomplish cell counting from transmitted-light microscope, automatically and effectively. In this work, a new deep-learning (DL)-based two-stage detection method (cGAN-YOLO) is designed to further enhance the performance of cell counting, which is achieved by combining a DL-based fluorescent image translation model and a DL-based cell detection model. The various results show that cGAN-YOLO can effectively detect and count some different types of cells from the acquired transmitted-light microscope images. Compared with the previously reported YOLO-based one-stage detection method, high recognition accuracy (RA) is achieved by the cGAN-YOLO method, with an improvement of 29.80%. Furthermore, we can also observe that cGAN-YOLO obtains an improvement of 12.11% in RA compared with the previously reported image-translation-based detection method. In a word, cGAN-YOLO makes it possible to implement cell counting directly from the experimental acquired transmitted-light microscopy images with high flexibility and performance, which extends the applicability in clinical research.
Automatic cell counting transmitted-light microscope deep-learning fluorescent image translation Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2023, 16(5): 2350004
西安理工大学陕西省超快光电与太赫兹科学重点实验室,陕西 西安 710048
基于太赫兹时域光谱(THz-TDS)系统,使用两个相互垂直的光电导天线构建了1×2 GaAs光电导太赫兹源阵列。通过调控各个阵元的偏置电压,对其辐射太赫兹波的偏振方向进行研究。结果表明:在已实现光电导发射天线阵列的高效合成以及可同时检测脉冲太赫兹波的振幅、相位及偏振态的探测天线的基础上,通过调控各个阵元的偏置电压分别改变了平行和垂直两个阵元辐射太赫兹波的强度;经过1×2 GaAs光电导太赫兹源阵列在远场的同步合成,可产生不同偏振方向的脉冲太赫兹波,实现了以全电控的方式产生任意偏振方向太赫兹波的光电导太赫兹辐射源。
太赫兹时域光谱系统 太赫兹辐射源 光电导天线阵列 偏振方向 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(18): 1811022





